Proba-3 will employ lasers to achieve millimeter accuracy in space.
Proba-3 will use laser for millimeter precision in space (Image Credit: Phys.org)
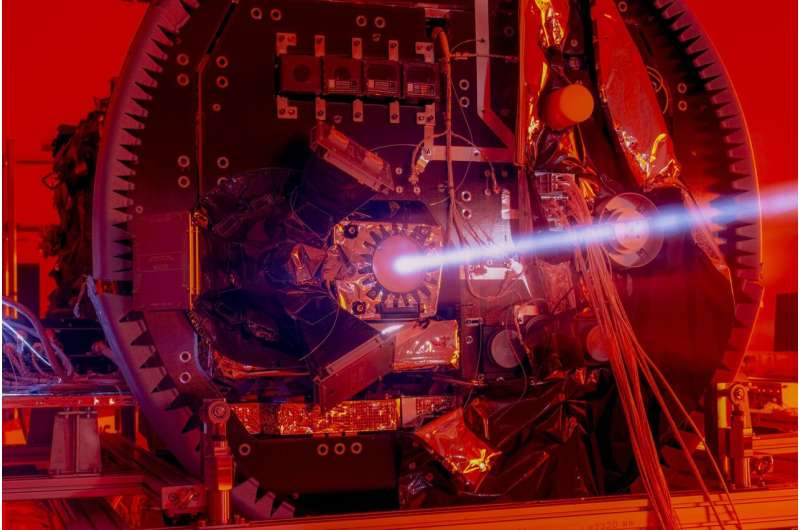
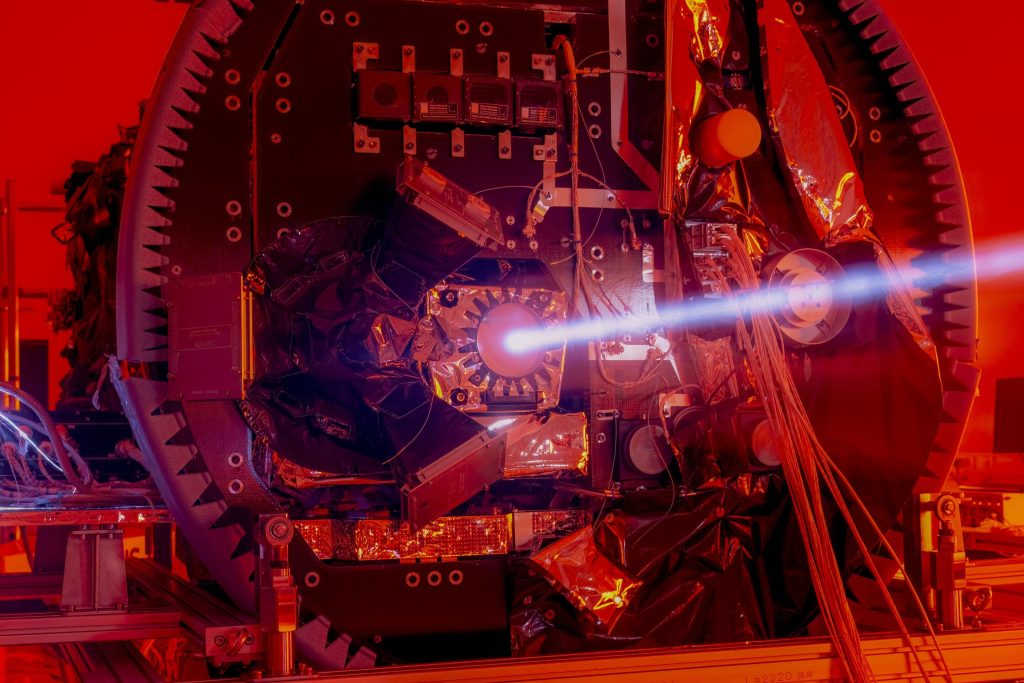
ESA’s double-spacecraft precision formation flying mission, Proba-3, is due to be launched from India on 4 December. The spacecraft pair will employ a set of positioning technologies to keep formation in space and this image shows the most precise: a laser shone from one platform to a retroreflector on the other. The reflected laser beam will provide positioning precision down to a single millimeter.
This infrared view of the reflected laser beam was acquired during on-ground calibration testing performed by ESA, MDA and Center Spatial de Liège personnel which took place at Redwire Space in Kruibeke, Belgium, back in February.
The goal of the mission is to achieve artificial solar eclipses on demand, as Proba-3’s Occulter spacecraft casting a precisely-controlled shadow onto its Coronagraph spacecraft for six hours at time.
To maintain the position of a shadow just 8 cm across on the Coronagraph satellite from the Occulter satellite around 150 m away, the two satellites rely on multiple sensors, including inter-satellite radio links, Global Navigation Satellite System receivers, visual imaging of LEDs and—for the most precise positioning at closest range—a laser metrology (or “measurement of measurement”) system.
The laser is seen being fired from the Occulter spacecraft towards the Coronagraph’s retroreflector, designed to reflect it back in precisely the same direction it originated from. In addition, a set of Shadow Position Sensors located around the coronagraph aperture will ensure the shadow remains in the correct position.
This mission is being put together for ESA by a consortium led by Spain’s SENER, with participation by more than 29 companies from 14 countries. The Proba-3 platforms have been designed by Airbus Defense and Space in Spain and satellite integration by Redwire in Belgium. GMV in Spain is responsible for Proba-3’s formation flying subsystem, while its main coronagraph instrument comes from Belgium’s Center Spatial de Liège, CSL.
Proba-3 is due to be launched via PSLV-XL launcher by the Indian Space Research Organization, ISRO.
Provided byEuropean Space Agency
Proba-3 will use laser for millimeter precision in space (2024, November 22)
retrieved 23 November 2024
from https://phys.org/news/2024-11-proba-laser-millimeter-precision-space.html
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.





