Small asteroid identified just hours before colliding with Earth, making it the fourth ‘imminent impactor’ of 2024.

Tiny asteroid detected hours before hitting Earth to become 4th ‘imminent impactor’ of 2024 (Image Credit: Space.com)
A tiny asteroid was detected on a collision course with Earth today (Dec. 3) and is expected to burn up in Earth’s atmosphere.
The asteroid measures around 27 inches (70 centimeters) wide and was detected by astronomers with the Kitt Peak National Observatory near Tucson, Arizona, a NOIRLab facility that is home to two radio telescopes and over a dozen optical telescopes. The small space rock should hit Earth’s atmosphere today around 11:15 a.m. ET (1615 GMT).
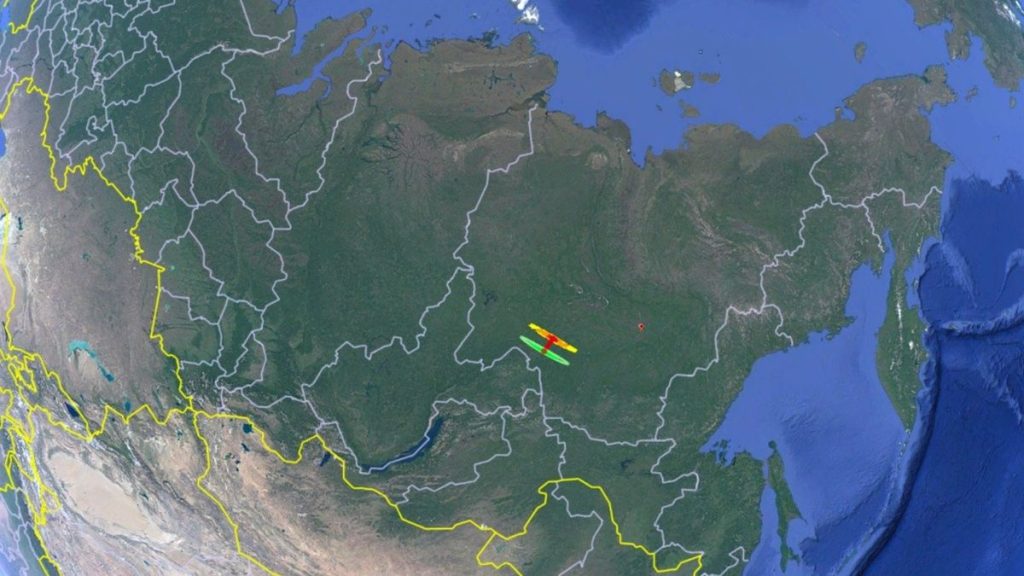
The asteroid is completely harmless and is expected to produce a “nice fireball in the sky over northern Siberia,” the European Space Agency wrote on X.
The asteroid, which has the temporary designation C0WEPC5, has now become the 4th “imminent impactor” discovered in 2024, meaning an asteroid that was discovered within hours of its expected impact. It was only the 11th confirmed imminent impactor overall (a 12th one has yet to be confirmed, according to physicist Richard Moissl).
☄️🎇Incoming! The 12th ever imminent impactor discovered before atmospheric entry is on it’s way to cause a harmless meteor in about 7 hours from now (~16:15 UTC +/- 5 minutes) over Siberia. With an estimated size of ~70 cm diameter it will cause a nice bright fireball #C0WECP5 pic.twitter.com/yY8IpUlZHeDecember 3, 2024
The third imminent impactor was asteroid 2024 UQ, discovered on Oct. 22 by the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) survey in Hawaii. It was discovered just two hours before it burned up over the Pacific Ocean over Hawaii.
The first of these imminent impactors this year was 2024 BX1, a 3.3-feet-wide (1 meter) asteroid that burned up harmlessly over Berlin in January. The second, 2024 RW1, exploded over the Philippines on Sept. 4 in a spectacular fireball that was caught on cameras and shared widely on social media.
The European Space Agency and other space agencies operate a multitude of sensor networks around Earth to keep an eye on incoming objects such as C0WEPC5.
Space agencies around the world are increasing efforts to keep an eye on and catalog the multitude of asteroids and other objects that either orbit or pass close to Earth through programs like the ATLAS survey, Catalina Sky Survey, ESA’s NEOCC and more.
NASA is also working on a new infrared telescope known as NEO Surveyor that will hunt for potentially threatening near-Earth objects.